Advancements in Understanding Neurogenesis in Alzheimer's Disease: Current Research and Insights
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71321/4gjht115Keywords:
Alzheimer's disease, Dentate gyrus, Neurogenesis, Rbm8a geneAbstract
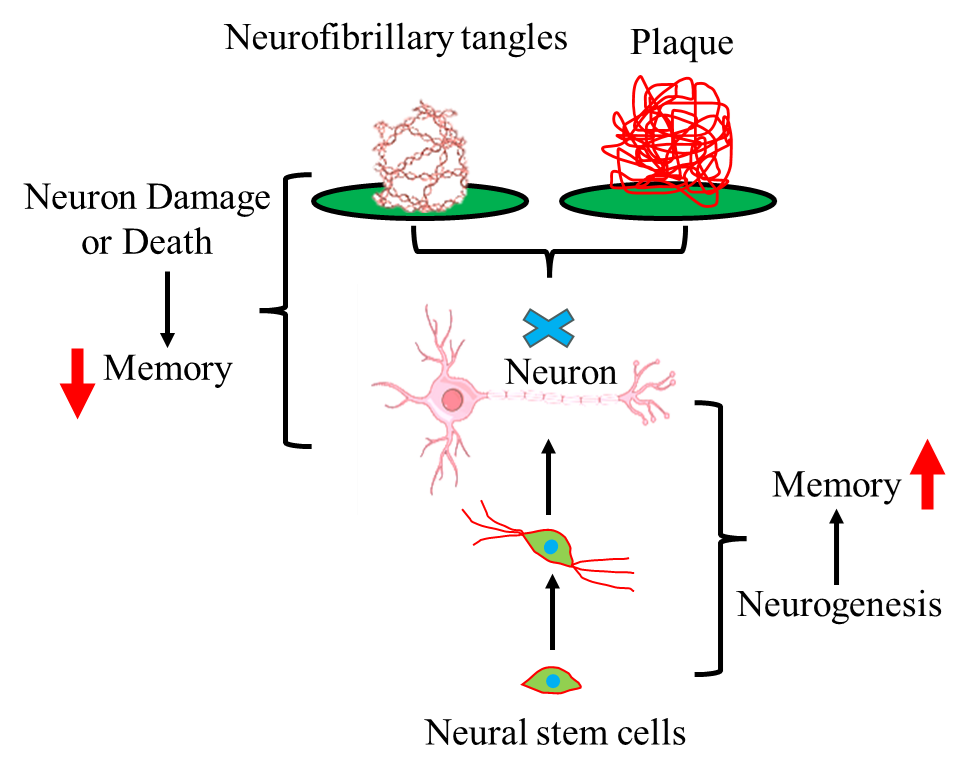
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is increasingly impacting the aging global population, with its prevalence and mortality rates rising steadily. This trend severely affects the quality of life and intensifies the economic strain on both families and society. Despite ongoing research, effective treatments remain elusive. However, enhancing neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG) to promote the formation of new neurons and replace those lost in AD patients' hippocampus holds promise as a potential strategy to improve cognitive and memory functions, offering hope for delaying or even treating the disease.
References
[1] Kuhn HG, Toda T, Gage FH. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis: A Coming-of-Age Story. J Neurosci. 2018;38(49):10401-10410.
[2] Guarnieri FC, de Chevigny A, Falace A, Cardoso C. Disorders of neurogenesis and cortical development. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018;20(4):255-266.
[3] Mercerón-Martínez D, Ibaceta-González C, Salazar C, Almaguer-Melian W, Bergado-Rosado JA, Palacios AG. Alzheimer's Disease, Neural Plasticity, and Functional Recovery. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;82(s1):S37-S50.
[4] Eratne D, Loi SM, Farrand S, Kelso W, Velakoulis D, Looi JC. Alzheimer's disease: clinical update on epidemiology, pathophysiology and diagnosis. Australas Psychiatry. 2018;26(4):347-357.
[5] Lane CA, Hardy J, Schott JM. Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Neurol. 2018;25(1):59-70.
[6] Raz L, Knoefel J, Bhaskar K. The neuropathology and cerebrovascular mechanisms of dementia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016;36(1):172-186.
[7] Hachinski V. Dementia: new vistas and opportunities. Neurol Sci. 2019;40(4):763-767.
[8] Winblad B, Amouyel P, Andrieu S, et al. Defeating Alzheimer's disease and other dementias: a priority for European science and society. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(5):455-532.
[9] Serrano-Pozo A, Das S, Hyman BT. APOE and Alzheimer's disease: advances in genetics, pathophysiology, and therapeutic approaches [published correction appears in Lancet Neurol. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20(1):68-80.
[10] Alzheimer's Association. 2018 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures[J]. Alzheimer's & Dementia, 2018, 14(3): 367-429.
[11] Keogh-Brown MR, Jensen HT, Arrighi HM, Smith RD. The Impact of Alzheimer's Disease on the Chinese Economy. EBioMedicine. 2015;4:184-190.
[12] Reiss AB, Arain HA, Stecker MM, Siegart NM, Kasselman LJ. Amyloid toxicity in Alzheimer's disease. Rev Neurosci. 2018;29(6):613-627.
[13] Zhang H, Zheng Y. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2019;41(5):702-708.
[14] Reiss AB, Arain HA, Stecker MM, Siegart NM, Kasselman LJ. Amyloid toxicity in Alzheimer's disease. Rev Neurosci. 2018;29(6):613-627.
[15] Quiroz YT, Sperling RA, Norton DJ, et al. Association Between Amyloid and Tau Accumulation in Young Adults With Autosomal Dominant Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2018;75(5):548-556.
[16] Tabatabaei-Jafari H, Shaw ME, Walsh E, Cherbuin N. Cognitive/Functional Measures Predict Alzheimer's Disease, Dependent on Hippocampal Volume. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2020;75(7):1393-1402.
[17] Jaroudi W, Garami J, Garrido S, Hornberger M, Keri S, Moustafa AA. Factors underlying cognitive decline in old age and Alzheimer's disease: the role of the hippocampus. Rev Neurosci. 2017;28(7):705-714.
[18] Balestrieri JVL, Nonato MB, Gheler L, Prandini MN. Structural Volume of Hippocampus and Alzheimer's Disease. Rev Assoc Med Bras . 2020;66(4):512-515.
[19] Sung PS, Lin PY, Liu CH, Su HC, Tsai KJ. Neuroinflammation and Neurogenesis in Alzheimer's Disease and Potential Therapeutic Approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):701.
[20] Berger T, Lee H, Young AH, Aarsland D, Thuret S. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Major Depressive Disorder and Alzheimer's Disease. Trends Mol Med. 2020;26(9):803-818.
[21] Moreno-Jiménez EP, Flor-García M, Terreros-Roncal J, et al. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is abundant in neurologically healthy subjects and drops sharply in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Nat Med. 2019;25(4):554-560.
[22] Niklison-Chirou MV, Agostini M, Amelio I, Melino G. Regulation of Adult Neurogenesis in Mammalian Brain. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):4869.
[23] Disouky A, Lazarov O. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2021;177:137-156.
[24] Richetin K, Steullet P, Pachoud M, et al. Tau accumulation in astrocytes of the dentate gyrus induces neuronal dysfunction and memory deficits in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Neurosci. 2020;23(12):1567-1579.
[25] Cope EC, Gould E. Adult Neurogenesis, Glia, and the Extracellular Matrix. Cell Stem Cell. 2019;24(5):690-705.
[26] Kuhn HG, Toda T, Gage FH. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis: A Coming-of-Age Story. J Neurosci. 2018;38(49):10401-10410.
[27] Anacker C, Hen R. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive flexibility - linking memory and mood. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017;18(6):335-346.
[28] Anacker C, Hen R. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive flexibility - linking memory and mood. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017;18(6):335-346.
[29] Sahab-Negah S, Hajali V, Moradi HR, Gorji A. The Impact of Estradiol on Neurogenesis and Cognitive Functions in Alzheimer's Disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020;40(3):283-299.
[30] Dard RF, Dahan L, Rampon C. Targeting hippocampal adult neurogenesis using transcription factors to reduce Alzheimer's disease-associated memory impairments. Hippocampus. 2019;29(7):579-586.
[31] Hollands C, Tobin MK, Hsu M, et al. Depletion of adult neurogenesis exacerbates cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease by compromising hippocampal inhibition. Mol Neurodegener. 2017;12(1):64.
[32] Ferreiro E, Lanzillo M, Canhoto D, et al. Chronic hyperglycemia impairs hippocampal neurogenesis and memory in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Neurobiol Aging. 2020;92:98-113.
[33] Amber S, Sumera, Mirza FJ, et al. Amyloid-beta Induced Neurotoxicity Impairs Cognition and Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Mouse Model for Alzheimer's Disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2020;17(11):1033-1042.
[34] Moreno-Jiménez EP, Flor-García M, Terreros-Roncal J, et al. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is abundant in neurologically healthy subjects and drops sharply in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Nat Med. 2019;25(4):554-560.
[35] Hollands C, Tobin MK, Hsu M, et al. Depletion of adult neurogenesis exacerbates cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease by compromising hippocampal inhibition. Mol Neurodegener. 2017;12(1):64.
[36] Unger MS, Marschallinger J, Kaindl J, et al. Early Changes in Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Transgenic Mouse Models for Alzheimer's Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(8):5796-5806.
[37] Choi S H, Bylykbashi E, Chatila Z K, et al. Combined adult neurogenesis and BDNF mimic exercise effects on cognition in an Alzheimer’s mouse model[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6406).
[38] Robinson JL, Molina-Porcel L, Corrada MM, et al. Perforant path synaptic loss correlates with cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease in the oldest-old. Brain. 2014;137(9):2578-2587.
[39] West MJ, Coleman PD, Flood DG, Troncoso JC. Differentielt neurontab i hippocampus hos normalt aldrende og hos patienter med Alzheimers sygdom [Differential neuronal loss in the hippocampus in normal aging and in patients with Alzheimer disease]. Ugeskr Laeger. 1995;157(22):3190-3193.
[40] Spalding KL, Bergmann O, Alkass K, et al. Dynamics of hippocampal neurogenesis in adult humans. Cell. 2013;153(6):1219-1227.
[41] Yi Y, Zhang Y, Song Y, Lu Y. Treadmill Running Regulates Adult Neurogenesis, Spatial and Non-spatial Learning, Parvalbumin Neuron Activity by ErbB4 Signaling. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jan 29;44(1):17.
[42] Zhang T, Ding H, Wang Y, Yuan Z, Zhang Y, Chen G, Xu Y, Chen L. Akt3-mTOR regulates hippocampal neurogenesis in adult mouse. J Neurochem. 2021 Nov;159(3):498-511.
[43] Yi Y, Song Y, Lu Y. Parvalbumin Interneuron Activation-Dependent Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Is Required for Treadmill Running to Reverse Schizophrenia-Like Phenotypes. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Feb 4;8:24.
[44] Wang P, Liang Y, Chen K, Yau SY, Sun X, Cheng KK, Xu A, So KF, Li A. Potential Involvement of Adiponectin Signaling in Regulating Physical Exercise-Elicited Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Dendritic Morphology in Stressed Mice. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Jul 3;14:189.
[45] Lattanzi D, Savelli D, Pagliarini M, Cuppini R, Ambrogini P. Short-Term, Voluntary Exercise Affects Morpho-Functional Maturation of Adult-Generated Neurons in Rat Hippocampus. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 20;23(12):6866.
[46] Vinogradova A, Sysova M, Smirnova P, Sidorova M, Turkin A, Kurilova E, Tuchina O. Enriched Environment Induces Sex-Specific Changes in the Adult Neurogenesis, Cytokine and miRNA Expression in Rat Hippocampus. Biomedicines. 2023 May 2;11(5):1341.
[47] Shixing X, Xueyan H, Yuan R, Wei T, Wei W. Enriched environment can reverse chronic sleep deprivation-induced damage to cellular plasticity in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus. Transl Neurosci. 2023 Mar 21;14(1):20220280.
[48] Vecchiarelli HA, Patel PP, Hill MN, Dyck RH. Environmental Enrichment Engages Vesicular Zinc Signaling to Enhance Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Cells. 2023 Mar 13;12(6):883.
[49] Zocher S, Overall RW, Lesche M, Dahl A, Kempermann G. Environmental enrichment preserves a young DNA methylation landscape in the aged mouse hippocampus. Nat Commun. 2021 Jun 23;12(1):3892.
[50] rońska-Pęski M, Gonçalves JT, Hébert JM. Enriched Environment Promotes Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis through FGFRs. J Neurosci. 2021 Mar 31;41(13):2899-2910.
[51] Wang H, Xu X, Xu X, Gao J, Zhang T. Enriched Environment and Social Isolation Affect Cognition Ability via Altering Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Density in Mice Hippocampus. Neurochem Res. 2020 Oct;45(10):2417-2432.
[52] Ma X, Xiao W, Li H, Pang P, Xue F, Wan L, Pei L, Yan H. Metformin restores hippocampal neurogenesis and learning and memory via regulating gut microbiota in the obese mouse model. Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Jul (95):68-83.
[53] Beltran-Casanueva R, Hernández-García A, de Amo García P, Blanco-Reina E, Serrano-Castro P, García-Casares N, Fuxe K, Borroto-Escuela DO, Narváez M. Neuropeptide Y receptor 1 and galanin receptor 2 (NPY1R-GALR2) interactions in the dentate gyrus and their relevance for neurogenesis and cognition. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Feb 14; 18:1323986.
[54] Miyata S, Tsuda M, Mitsui S. Overexpression of Motopsin, an Extracellular Serine Protease Related to Intellectual Disability, Promotes Adult Neurogenesis and Neuronal Responsiveness in the Dentate Gyrus. Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Dec 28.
[55] Willinger Y, Friedland Cohen DR, Turgeman G. Exogenous IL-17A Alleviates Social Behavior Deficits and Increases Neurogenesis in a Murine Model of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 28;25(1):432.
[56] Sugaya K, Vaidya M. Stem Cell Therapies for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1056 :61-84.
[57] Penney J, Ralvenius WT, Tsai LH. Modeling Alzheimer's disease with iPSC-derived brain cells. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(1):148-167.
[58] Wang C, Ward ME, Chen R, et al. Scalable Production of iPSC-Derived Human Neurons to Identify Tau-Lowering Compounds by High-Content Screening. Stem Cell Reports. 2017;9(4):1221-1233.
[59] mponsah AE, Guo R, Kong D, et al. Patient-derived iPSCs, a reliable in vitro model for the investigation of Alzheimer's disease. Rev Neurosci. 2021;32(4):379-402.
[60] Kondo T, Imamura K, Funayama M, et al. iPSC-Based Compound Screening and In Vitro Trials Identify a Synergistic Anti-amyloid β Combination for Alzheimer's Disease. Cell Rep. 2017;21(8):2304-2312.
[61] Nakano M, Kubota K, Kobayashi E, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve cognitive impairment in an Alzheimer's disease model by increasing the expression of microRNA-146a in hippocampus. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):10772.
[62] Tanila H. The role of BDNF in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2017;97(1):114-118.
[63] Caffino L, Mottarlini F, Fumagalli F. Born to Protect: Leveraging BDNF Against Cognitive Deficit in Alzheimer's Disease. CNS Drugs. 2020;34(3):281-297.
[64] Nakano M, Kubota K, Kobayashi E, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve cognitive impairment in an Alzheimer’s disease model by increasing the expression of microRNA-146a in hippocampus[J]. Scientific reports, 2020, 10(1): 1-15.
Type
Published
Data Availability Statement
The manuscript submitted this time is a review and does not involve confidential data. The detailed content can be obtained through the manuscript
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Brain Conflux

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







