De Novo Mutation of POLR3A Associated with 4H Leukodystrophy Syndrome: A Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71321/tcff0843Keywords:
POLR3A, Gene Function, 4H leukodystrophy syndromeAbstract
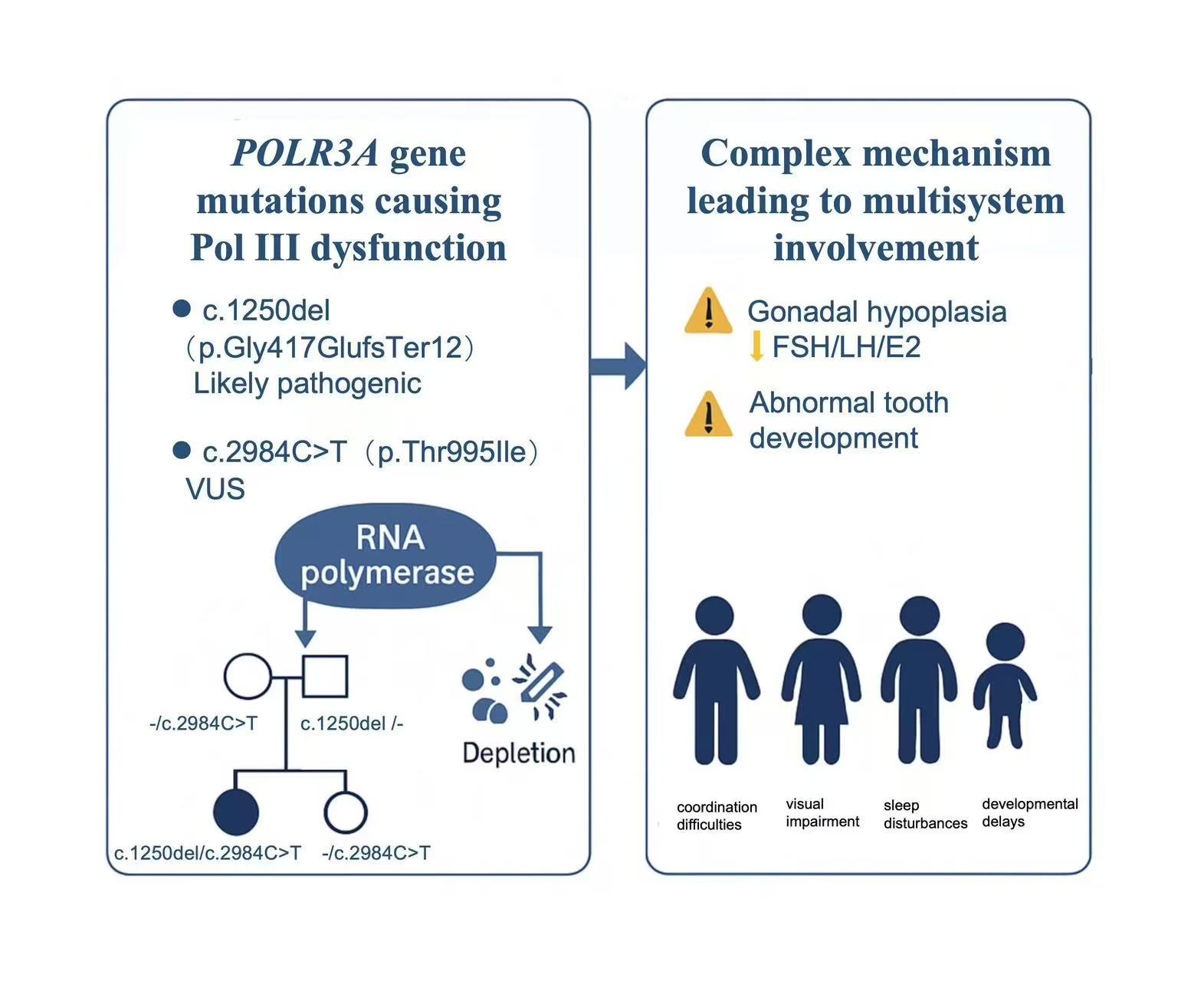
Background: Pathogenic biallelic variants in POLR3A have been associated with different disorders characterized by progressive neurological deterioration. These include the 4H leukodystrophy syndrome (hypomyelination, hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, and hypodontia) and adolescent-onset progressive spastic ataxia, as well as Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch syndrome (WRS), a recognizable neonatal progeroid syndrome. The phenotypic differences between these disorders are thought to occur mainly due to different functional effects of underlying POLR3A variants.
Case presentation: Here, we present the detailed clinical course of a 20-year-old woman who presented with developmental delays, neurological deficits, metabolic abnormalities, and sleep disturbances. She was born to non-consanguineous parents and had an elder sister who usually behaved. Laboratory studies demonstrated low or undetectable LH and FSH levels and abnormally low estradiol levels. MRI showed leukoencephalopathy characterized by white matter lesions and brain atrophy. Homozygous missense mutation c.2984C>T (p.Thr995Ile) was found in POLR3A, which codes for the largest subunit of RNA polymerase Ill.
Conclusions: POLR3A-induced leukodystrophy is relatively rare and not well understood, making it challenging to diagnose and easy to overlook. The prognosis for this disease is generally poor, significantly impacting the quality of life of affected individuals. Since Pol III-related leukodystrophies shows various combination of neurologic and non-neurologic features, additional report will help to bring crucial information concerning this molecular diagnosis, the prediction of the disease and practical consequences for genetic counseling.
References
[1] Tétreault, M., Choquet, K., Orcesi, S., Tonduti, D., Balottin, U., Teichmann, M., Fribourg, S., Schiffmann, R., Brais, B., Vanderver, A., & Bernard, G. (2011). Recessive mutations in POLR3B, encoding the second largest subunit of Pol III, cause a rare hypomyelinating leukodystrophy. American journal of human genetics, 89(5), 652–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.10.006
[2] Saitsu, H., Osaka, H., Sasaki, M., Takanashi, J., Hamada, K., Yamashita, A., Shibayama, H., Shiina, M., Kondo, Y., Nishiyama, K., Tsurusaki, Y., Miyake, N., Doi, H., Ogata, K., Inoue, K., & Matsumoto, N. (2011). Mutations in POLR3A and POLR3B encoding RNA Polymerase III subunits cause an autosomal-recessive hypomyelinating leukoencephalopathy. American journal of human genetics, 89(5), 644–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.10.003
[3] McKenna, M. C., O'Connor, A., Lockhart, A., Bogdanova-Mihaylova, P., Brett, F., Langan, Y., Meaney, J., Costigan, D., Doherty, C. P., Bede, P., Murphy, S. M., & Hutchinson, S. (2024). POLR3A-related disorders: expanding the clinical phenotype. Journal of neurology, 271(6), 3635–3638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-024-12265-9
[4] Wolf, N. I., Vanderver, A., van Spaendonk, R. M., Schiffmann, R., Brais, B., Bugiani, M., Sistermans, E., Catsman-Berrevoets, C., Kros, J. M., Pinto, P. S., Pohl, D., Tirupathi, S., Strømme, P., de Grauw, T., Fribourg, S., Demos, M., Pizzino, A., Naidu, S., Guerrero, K., van der Knaap, M. S., … 4H Research Group (2014). Clinical spectrum of 4H leukodystrophy caused by POLR3A and POLR3B mutations. Neurology, 83(21), 1898–1905. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001002
[5] Harting, I., Al-Saady, M., Krägeloh-Mann, I., Bley, A., Hempel, M., Bierhals, T., Karch, S., Moog, U., Bernard, G., Huntsman, R., van Spaendonk, R. M. L., Vreeburg, M., Rodríguez-Palmero, A., Pujol, A., van der Knaap, M. S., Pouwels, P. J. W., & Wolf, N. I. (2020). POLR3A variants with striatal involvement and extrapyramidal movement disorder. Neurogenetics, 21(2), 121–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-019-00602-4
[6] Thiffault, I., Wolf, N. I., Forget, D., Guerrero, K., Tran, L. T., Choquet, K., Lavallée-Adam, M., Poitras, C., Brais, B., Yoon, G., Sztriha, L., Webster, R. I., Timmann, D., van de Warrenburg, B. P., Seeger, J., Zimmermann, A., Máté, A., Goizet, C., Fung, E., van der Knaap, M. S., … Bernard, G. (2015). Recessive mutations in POLR1C cause a leukodystrophy by impairing biogenesis of RNA polymerase III. Nature communications, 6, 7623. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8623
Type
Published
Data Availability Statement
Additional data related to this paper may be requested from the authors.
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Brain Conflux

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







