ATPexGen: ATP-induced cell death database
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71321/rwcd3q57Keywords:
ATPexGen:ATP-induced cell death, Database, Gene silencing, CTD, BioGRIDAbstract
ATPexGen aims to establish a comprehensive database dedicated to ATP-induced cell death, addressing a critical gap in biomedical research. While ATP is the primary energy source for cells, its role in regulating cell death remains underexplored. Existing databases lack the systematic and detailed data required to support advanced research in this area. ATPexGen will integrate cutting-edge experimental data and literature, creating a multi-dimensional information platform to enhance understanding of ATP's role in cell death mechanisms. This platform will not only advance fundamental research but also facilitate drug development and therapeutic innovations. Given the global prevalence of cell death-related diseases, the development of ATPexGen is both urgent and impactful, offering robust support and valuable references for advancing research and clinical applications in this critical field.
References
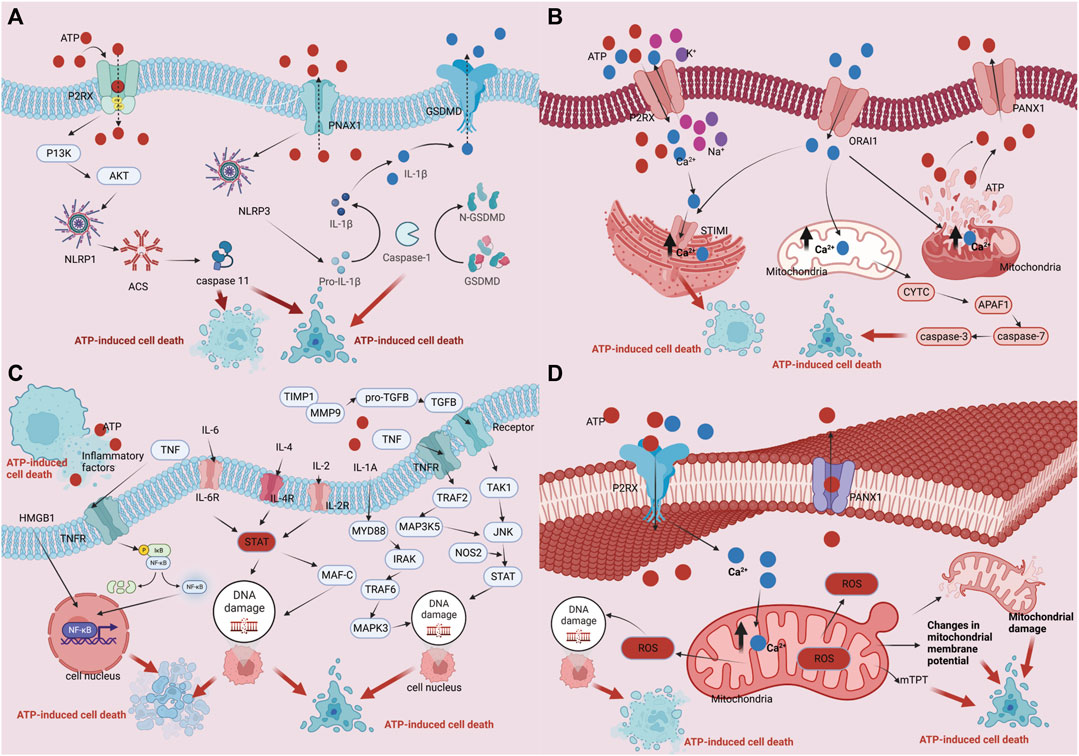
[1] Wang, W., Zhang, H., Sandai, D., Zhao, R., Bai, J., Wang, Y,, et al.(2023). ATP-induced cell death: a novel hypothesis for osteoporosis. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology, 11, 1324213.https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2023.1324213.
[2] HL Zhang, D Sandai, ZW Zhang, ZJ Song, D Babu, Y Tabana,, et al. (2023). Adenosine triphosphate induced cell death: Mechanisms and implications in cancer biology and therapy. World journal of clinical oncology, 14(12), 549. https://doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v14.i12.549.
[3] HL Zhang, S Doblin, ZW Zhang, ZJ Song, B Dinesh, Y Tabana,, et al. (2024). Elucidating the molecular basis of ATP-induced cell death in breast cancer: Construction of a robust prognostic model. World Journal of Clinical Oncology, 15(2), 208. https://doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v15.i2.208.
[4] Zhang H, Sandai D, Zhang Z,Song Z,Zhang H, Zhao R,et al.(2023). ATP-induced cell death mechanism. Int J Biol Life Sci, 4, 15-6.
[5] W Wang, XM Wang, HL Zhang, R Zhao, Y Wang, HL Zhang, et al. (2024). Molecular and metabolic landscape of adenosine triphosphate-induced cell death in cardiovascular disease. World Journal of Cardiology, 16(12), 689. https://doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v16.i12.689.
[6] Z Zhang, H Zhang, Z Zhang, D Sandai, P Lu, H Zhang, et al. (2024). Identification and validation of mRNA profiles linked to ATP-induced cell death represent a novel prognostic model for breast cancer. Frontiers in Immunology, 15, 1483498. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1483498.
[7] H Zhang, H Zhang, R Zhao, D Sandai, Z Song, Z Zhang, et al. (2024). ATP Cellotoxicity, ATP-Induced Cell Death and ATP Depletion[J]. International Journal of Public Health and Medical Research, 1(2): 35-38.
Type
Published
Data Availability Statement
All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are present in the paper or the Supplementary Materials. Additional data related to this paper may be requested from the authors.
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Life Conflux

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







